What Assets Should I Track for IT Budgeting and Planning?
Failing to plan is planning to fail. The costliest way to maintain your IT infrastructure is to ignore risk and only replace systems after they break.
Predicting recurring and future IT costs can be challenging, especially if you’re not a tech expert. Using outdated hardware and software beyond their lifespan can pose significant risks.
We offer budgeting and lifecycle planning to keep you informed about your IT assets, helping you make timely updates and avoid costly surprises.
If you prefer to handle this yourself, here are the assets you should be tracking and the detailed information to gather for each one.
What are My IT Assets?
IT assets include all the technological equipment you depend on to run your business, from servers and computers to firewalls and switches, as well as applications and databases.
Start with the major items and work your way down to the smaller ones. It’s important to note that some items, like mice, keyboards, docking stations and monitors, don’t need to be tracked as they won’t significantly impact your budget.
“When planning your IT budget and tracking assets, it’s crucial to remember that the type of asset isn’t the only factor to consider. The level of risk each specific asset poses to your day-to-day operations is equally important.”
Trying to list everything is a bad way to start; it can quickly become overwhelming and lead to inefficiencies. Instead, focus on the essentials that truly impact your IT budget and operations.
Here is a practical list of top 10 most important assets you should be tracking:
- Servers (Physical and Virtual): Physical servers, virtual servers, and their associated hardware.
- Workstations: Desktops, laptops, and other user-facing computers.
- Battery Backup (UPS): Uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) that protect against power outages.
- Backup Appliances: Devices and systems used for data backup and disaster recovery.
- Firewalls: Network security devices that monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic.
- Switches: Networking hardware that connects devices within a local area network (LAN).
- Wireless Access Points (APs): Devices that allow wireless devices to connect to a wired network using Wi-Fi.
- Phones: Business telephony systems, including IP phones.
- Printers: Office printers, especially those critical for business operations.
- Software: Important software licenses, including operating systems and application software.
What Information Needs to Be Tracked?
For each IT asset, track the following information:
- Type
- Purchase date/estimated age
- Estimated cost
- Name
- Manufacturer
- Model
- Serial number or other unique identifiers
- Budgeted replacement date
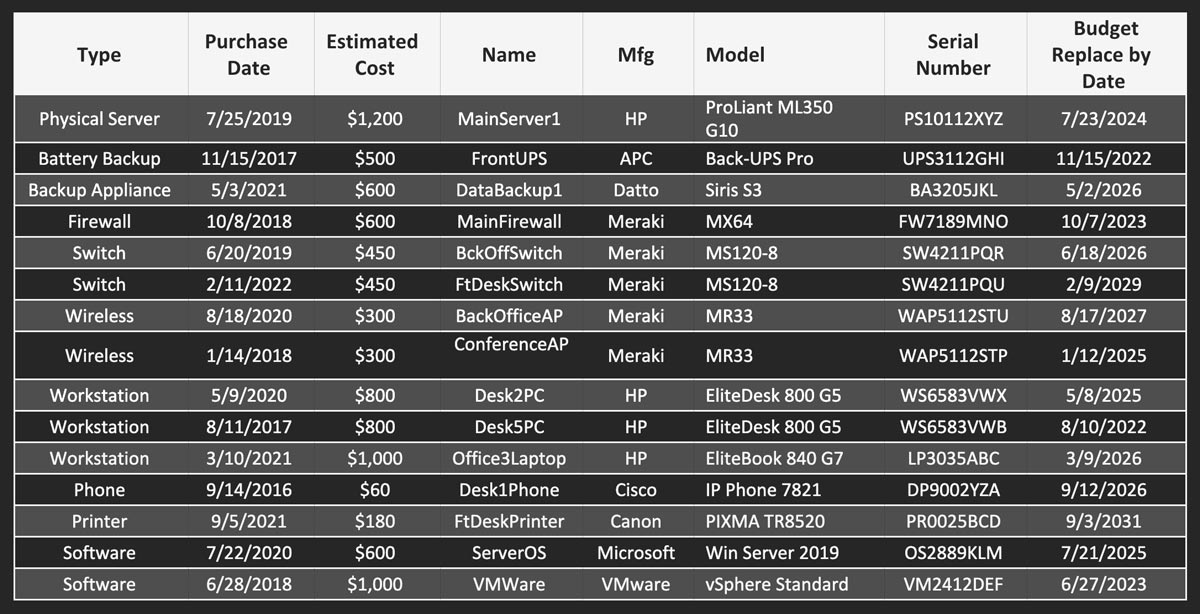
Below, is a sample table of what an organization’s tracked assets might look like:
Lifespan of IT Assets
Each asset has an average lifespan that helps determine when you should replace it:
- 3-5 years: servers (physical and virtual), UPS, storage, backups, firewalls, workstations
- 5-7 years: switches, wireless, phones, printers
Replacing assets on schedule can prevent unexpected failures. If multiple expenses are coming up all at once, we can adjust replacement dates to balance risk and costs.
Estimating Your IT Assets
Per Location:
- Servers: The average small business probably has 1-3 servers, each costing a few thousand dollars.
- Firewalls: Typically 1 per location, sometimes 2 for redundancy in larger spots.
- Battery Backup (UPS): 1 per server/network rack. Costs a few hundred to over a thousand each.
Per Device:
- Switches: Usually 1 switch per 10-15 workstations or devices, with costs ranging from a few hundred to a few thousand each.
- Wireless Access Points (APs): Typically 1 per 10-15 users or devices, with a cost of a few hundred bucks each.
- Backup Appliances: Usually 1-2 needed per organization. Pricey but necessary for data protection.
- Printers: Costs depend on the number of printers, with multifunctional printers being more expensive but fewer in quantity.
Per Employee:
- Workstations: generally 1 per employee. This is a significant budget item due to the number required.
- Phones: 1 per employee, typically cheaper, but the total cost scales with the number of employees.
Assessing Asset Importance and Risk
When planning your IT budget and tracking assets, it’s crucial to remember that the type of asset isn’t the only factor to consider. The level of risk each specific asset poses to your day-to-day operations is equally important.
For example, not all switches hold the same risk; a core switch connecting your entire network to the internet is far more critical than an edge switch used for a single computer in the warehouse. Evaluating both the asset type and its impact on your production will help you prioritize replacements and investments more effectively.
Additionally, consider the manufacturer’s end-of-support date. Running unsupported equipment presents a different category of risk compared to simply using old equipment.
Evaluating both the asset type and its impact on your production, along with support status, will help you prioritize replacements and more effectively.
Need Help Tracking Your IT Assets?
Tracking IT assets can be daunting, but knowing what you have, how old it is and when it should be replaced will save you headaches down the road.
The costliest way to maintain your IT infrastructure is to ignore risks and only replace systems after they break.
Contact us here to find out how we can keep your business running smoothly while increasing productivity, security and profitability.
Did you like this blog? You can subscribe to our newsletter to receive a weekly email with our latest blog posts.











